Shoulder Arthroscopy
Introduction
Arthroscopy is a procedure used for both diagnosis and treatment of joint problems. It is used mainly for any of the six joints namely shoulder, knee, wrist, elbow, ankle or hip. Arthroscopy procedure for shoulder is known as shoulder arthroscopy. It is done using a pen-thick instrument called Arthroscope. Arthroscope consists of a lens, a light system and a camera. It is considered more reliable than other methods of diagnosis such as X-rays. It is used to treat disease condition and injury involving bone, cartilage, tendon, ligament and muscle of the joints.
Indications
Shoulder arthroscopy is used to treat number of shoulder disease conditions such as:
Shoulder Impingement: Shoulder impingement occurs when the tendons of the rotator cuff rub against the bony protuberance called acromion causing pain. It occurs due to bone growth at the acromion called bone spur. Arthroscopy involves removal of the front part of the acromion process and some of the underlying tissue of the bursa (the fluid filled sac between the rotator cuff and the underlying bony structure).
Rotator cuff tear occurs when the four tendons surrounding the ball and socket joint of the shoulder are torn. This may occur due to injury or lifting heavy weight with a sudden jerk or due to degeneration of the tendons as one age. Arthroscopy is recommended if the tear is large or no improvement is seen with other non-surgical methods. The torn tendons are repaired through arthroscopy.
Frozen shoulder causes pain and stiffness of the shoulder joint. It may occur due to age and is more often seen in people above 40 years. People with diabetes or heart disease are more prone to frozen shoulder. It may also occur after some shoulder surgery or injury. In frozen shoulder the capsule of supporting soft tissue surrounding the ball and socket joint contracts and becomes inflamed .Moreover formation of adhesion occurs which further restrict the movement at the joint. Surgery is recommended when other treatments do not provide relief. Through arthroscopy the adhesions are cut and the inflamed tissues are removed.
Shoulder Instability occurs when the head of the upper arm bone slips out of the socket of the shoulder blade’s glenoid cavity either due to some injury or overuse. Arthroscopy is used in shoulder instability to repair damaged or stretched ligament or torn labrum (the fibroconnective tissue surrounding the glenoid cavity) to the bone.
Bicep rupture occurs when the tendons attaching the bicep muscle to the shoulder or elbow tears. It is of two types depending on whether the rupture of tendons is at the shoulder (proximal bicep tear) or at the elbow (distal bicep tear). In proximal bicep tear usually only one out of the two bicep tendon tears and since one is still intact the shoulder and arm function are not affected much. Surgery is done only if the patient is young and leads an active life. Distal bicep rupture is more often repaired surgically through arthroscopy as the muscle is attached to the elbow by only one tendon.
Pre-surgical instructions
- Inform the doctor about any medical condition with which currently suffering such as diabetes or heart disease
- Inform him about any medicines ,supplements or over the counter products currently taking
- Avoid smoking as it delays the healing of bones and wound.
- Tell the doctor about any general illness you had in the last 15 days such as fever, cold or herpes infection
- Stop taking medicines which thin the blood or increases the blood clotting time, 15 days before the surgery
Procedure
On the day of surgery, patient should follow the following instructions:
- Should not eat or drink 12 hour before the surgery
- Should wear loose comfortable clothes to the hospital
- Should not wear contact lens or jewelry or make up
- Any medicine to be taken before the surgery should be taken only with a sip of water
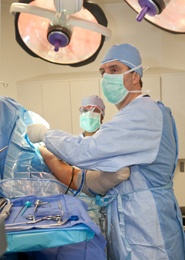
Either general anesthesia is given or the regional anesthesia is given to numb the shoulder and the arm. Sedation is also given to put the patient to sleep if only regional anesthesia is given. The fluid is injected into the shoulder to expand the shoulder joint to get a clear view and working space. A button sized hole is made in the shoulder and arthroscope is inserted through the hole. Fluid flows through the arthroscope and provides the surgeon with a clear view of the inside of the shoulder joint. It also minimizes bleeding. The surgeon can see the images from the arthroscope on the monitor. If necessary surgical instruments are introduced in the joint through separate holes one or three depending on the type of repair need to be done in the joint. After surgery the incisions are closed by giving stitches or with small sterile bandage strips. One is kept in the hospital for few hours after the surgery for observation and is discharged the same day.
Post-surgical instructions
After the surgery small surgery wounds take few days to heal and the surgical dressing is replaced by the simple band aids. The recovery time depends on the type and extent of problem for which the procedure was done. Pain medications are given. The arm of the affected shoulder is tied in a sling for a period as recommended by the doctor. Physical therapy is advised to improve shoulder mobility and strength after the surgery.
Few precautions that need to be taken after the surgery:
- Avoid lying flat on the bed as getting up will puts extra strain on the shoulder. Prefer to use reclining chair or some extra pillows to prop up the bed near the head for few days after the surgery.
- Do not use the arm for which surgery is done.
Advantages
The advantages of arthroscopy are less pain and complications after the procedure as compared to an open surgery. However if injury is more, open surgery is the only option for treatment. Healing time after arthroscopy depends on the amount of repair that was done using the procedure and may vary from case to case.
Risks and Complications
Complications of shoulder arthroscopy are infection, bleeding, damage to any nerve or blood vessel or delayed healing after the surgery. In certain cases stiffness of shoulder joint may occur after the surgery.
Call the doctor after the surgery if
- You have fever higher than 101 degree F
- There is excessive bleeding from the site of surgery
- Yellowish discharge from the wounds
- Redness , pain or swelling in the wounds
- Swelling in the arm which was operated
- Fingers appear dark in color
- Feeling of tingling or numbness in fingers of the treated arm
Summary
Thus shoulder arthroscopy is a minimum invasive surgery procedure used to see into the shoulder joint and repair damaged bone, muscle, tendon or ligament of the joint. It is done as an outpatient procedure and is safer than open shoulder surgery.
 Minimally Invasive Carpal Tunnel Technique in 3D
Minimally Invasive Carpal Tunnel Technique in 3D
